ADE Assay Services
ADE ASSAY SERVICE
Get Your ADE Assay Done Perfectly
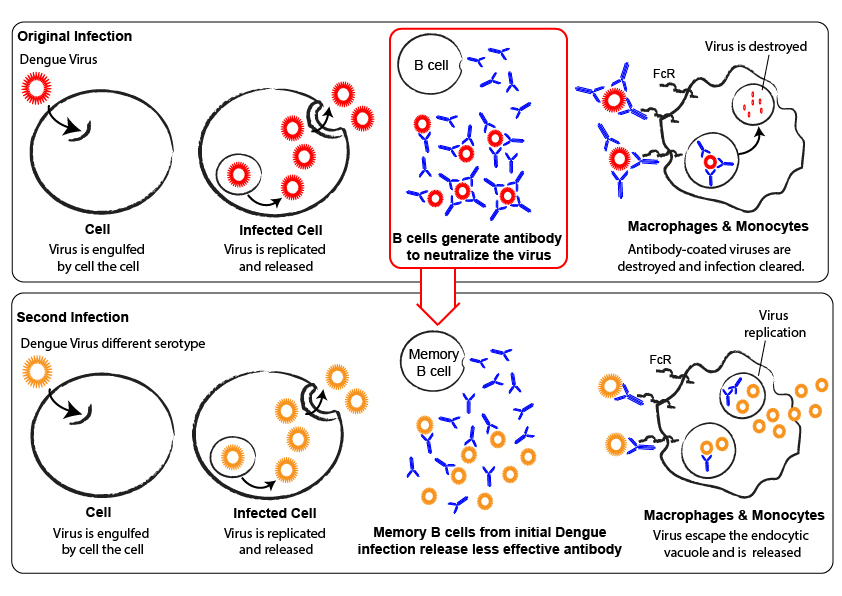
Antibody-dependent enhancement is a phenomenon by which non-neutralising antibodies bind to the virus and are then internalised by cells carrying the Fc Receptor, causing concomitant internalisation of the bound virus. If these cells (often macrophages) are permissive to viral replication, the antibodies will enhance infection by increasing virus entry.
This phenomenon is particularly well described for dengue, where different serotypes cause non-neutralizing antibody cross-reactivity, and ADE is one of the major issues in the development of certain therapeutics.
As ADE has been shown to be dependent both on antibody concentration and neutralizing properties, it is important to assess the impact of the antibody response induced by a certain immunization regime on ADE.
Our Approach
How our ADE assays are done.
ADE assays consist of the pre-incubation of a serial dilution of serum/antibody with a fixed concentration of virus, upon which the mix is added onto cells carrying the Fc Receptor. ADE is measured by comparing the percentage of infected cells at different serum concentrations with untreated/non-enhancing controls.
In our ADE assay, infection is quantified my immunostaining and flow cytometry analysis. The assay is internally controlled using known concentrations of purified enhancing and isotype antibodies. Untreated and uninfected controls are included in each plate to control for assay variability across plates.
The assay is optimised in a 96-well plate format to reduce the volume of testing material required, which in turn allows for parallel neutralisation tests and/or multiple replicates/repeats for increased robustness.
All about ADE
Subscribe

